Show Key Points
CBSE 12th Physics Exam: The CBSE Class 12 Physics exam is scheduled for February 20, 2025 (Friday). As a crucial subject, Physics significantly contributes to boosting overall board exam scores. To ensure students prepare effectively, we have made available a CBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper. This expert-designed resource is perfectly suited for last-minute revision and focused practice on important questions.
The provided sample paper is complete with solutions that offer clear explanations of the correct answers. Students are advised to download the CBSE Class 12 Physics Paper PDF using the links below. Utilizing this resource is an excellent way to strengthen your preparation and achieve high marks in the upcoming board examination.
CBSE Class 12 Physics 2026: Key Highlights
Check the table below to know the key pointers of CBSE 12 Physics 2026:
| Overview | Details |
| Board Name: | Central Board of Secondary Examination (CBSE) |
| Class: | 12 |
| Subject: | Physics |
| Subject Code: | 042 |
| Exam Date | 20th February, 2026 |
| Exam Time | 10:15 AM to 1:30 PM |
| Total Marks: | 100 |
| Theory Marks: | 70 |
| Project Marks: | 30 |
| Exam Duration: | 3 Hours |
| Official Website: |
CHECK: CBSE Class 12 Physics Last 10 Days Study Plan for Board Exam 2026
CBSE Class 12 Physics: Chapter-Wise Exam Pattern & Marking Scheme
Check the table below that outlines the CBSE 12th Physics Exam Pattern 2026. This Exam Pattern is taken from the CBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Papers and Previous Year Question Papers.
| Sections | Type and Number of Questions | Marks (Per Question) | Weightage (Total Marks) |
| A | 16 Questions | 1 | 16 |
| B | 5 Questions | 2 | 10 |
| C | 7 Questions | 3 | 21 |
| D | 2 Case Study-Based Questions | 4 | 8 |
| E | 3 Long Answer Questions | 5 | 15 |
| Total Marks |
|
| 70 |
CHECK: CBSE Class 12 Physics Exam Pattern 2026
CBSE Class 12 Physics 2026: Unit-wise Marks distribution
The theory portion of CBSE Class 12 Physics is worth a total of 70 marks. The practicals account for the final thirty points. The chapter-by-chapter exam format and grading system for CBSE Class 12 Physics are described below:
| Unit | Topics | Marks |
| Unit-1: Electrostatics | Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields | 16 |
| Chapter 2: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance | ||
| Unit-2: Current Electricity | Chapter 3: Current Electricity | |
| Unit-3: Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism | Chapter 4: Moving Charges and Magnetism | 17 |
| Chapter 5: Magnetism and Matter | ||
| Unit-4: Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents | Chapter 6: Electromagnetic Induction | |
| Chapter 7: Alternating Current | ||
| Unit-5: Electromagnetic Waves | Chapter–8: Electromagnetic Waves | 18
|
| Unit-6: Optics | Chapter–9: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments | |
| Chapter–10: Wave Optics | ||
| Unit-7: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter | Chapter–11: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter | 12
|
| Unit-8: Atoms and Nuclei | Chapter–12: Atoms | |
| Chapter–13: Nuclei | ||
| Unit-9: Electronic Devices | Chapter 7 –14: Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits | 7 |
CBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper 2026
Check and download the Class 12 Physics sample Paper to Boost your preparation for the upcoming CBSE Class 12 Physics Exam 2026:
SECTION A
| Sl. No. | Questions | Marks |
| 1. | The ratio of the nuclear densities of two nuclei having the mass numbers 8 and 27 is (A) 8:27 (B) 3:2 (C)2:3 (D) 1:1 | 1 |
| 2. | Two small identical magnets are allowed to fall freely, one through a vertical solenoid of 20 m made up of copper and another in air through the same vertical distance. The time taken by the two magnets to fall will be (A) same in both the cases. (B) more for the magnet falling in air. (C) more for the magnet falling through the solenoid. (D) infinite. | 1 |
| 3. | | 1 |
| 4. | Which of the following statements is not true for nuclear forces? (A) They are stronger than Coulomb forces. (B) They have about the same magnitude for different pairs of nucleons. (C)They are always attractive. (D)They saturate as the separation between two nucleons increases. | 1 |
| 5. | A charged particle is projected along the axis of a current carrying loop. Which of the following statements is true? (A) The acceleration of the charged particle will depend on the velocity with which it is projected. (B) The acceleration of the charged particle will depend on the magnitude of the current passing through the coil. (C) The acceleration of the charged particle will depend on the radius of the coil. (D) The charged particle will move with constant velocity. | 1 |
| 6. | When we move magnetic compass from point P to Q then which of the following statement is true (A) The deflection of the magnetic needle at P and Q will be in the same direction. (B) The deflection of the magnetic needle at P and Q will be in the opposite directions. (C) The deflection of the magnetic needle at P and Q will be perpendicular to each other. (D) The deflection of the magnetic needle at P and Q will be inclined at 45o with respect to each other. | 1 |
| 7. | Consider the diffraction pattern obtained from the sunlight incident on a pinhole of diameter 0.1 μm. If the diameter of the pinhole is slightly increased, it will affect the diffraction pattern such that: (A) its size decreases, and intensity decreases (B) its size increases, and intensity increases (C) its size increases, but intensity decreases (D) its size decreases, but intensity increases | 1 |
| 8. | If the phasor diagram for a device connected to AC supply is as shown in the fig, then which of the following statements is true? (A) When the frequency of the AC source is increased then the impedance of the device decreases. (B) This device behaves as conducting wire when connected across a DC source. (C) When the frequency of the AC source is decreased then the impedance of the device decreases. (D) D. This device stores energy in the form of magnetic potential energy. | 1 |
| 9. | Which of the following statements is true for the radio waves and the gamma rays? (A) The energy of gamma rays is lesser than that of the radio waves. (B) The frequency of the radio waves is higher than that of gamma rays. (C) The radio waves and the gamma rays have the same energy. (D) The energy of radio waves is lesser than that of the gamma rays. | 1 |
| 10. | The electron in a hydrogen atom makes a transition from an excited state to the ground state. Which of the following statements is true? (A) Its kinetic energy increases and its potential and total energies decrease. (B) Its kinetic energy decreases, potential increases and its total energy remains the same (C) Its kinetic energy and total energies decrease, and its potential energy increases. (D) Its kinetic potential and total energies decrease. | 1 |
| 11. | | 1 |
| 12. | If a charged hollow sphere and a solid sphere of aluminum and copper of equal radii are in electrostatic equilibrium, then which of the following statements is true? (A) Both the spheres are having equal charges. (B) The hollow sphere will have more charge than a solid sphere at its surface. (C) The aluminum sphere will have more charge on its surface than the copper sphere. (D) If a hollow sphere is also made up of aluminum then it will have more charge. | 1 |
| For Questions 13 to 16, two statements are given one labelled Assertion (A) and other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the options as given below. (A) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. (B) Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. (C) Assertion is true but Reason is false. (D) Both Assertion and Reason are false. | ||
| 13. | Assertion (A): For three point charges to be in equilibrium, they must be collinear. Reason(R): One of the three charges must have different polarity than the rest of the two. | 1 |
| 14. | Assertion (A): Total energy of an electron in a hydrogen atom is negative. Reason (R): The centripetal force is provided by electrostatic force. | 1 |
| 15. | Assertion (A): In interference and diffraction of light, light energy reduces in one region producing a dark fringe. It increases in another region and produces a bright fringe. Reason(R): This happens because energy is not conserved in the phenomena of interference and diffraction. | 1 |
| 16. | Assertion (A): A positive charge in an electric field moves along the direction of the electric field. Reason (R): On a positive charge a force acts in the direction of the electric field. | 1 |
SECTION B
| Sl. No. | Question | Marks |
| 17. | A potential difference of V volts is applied to a conductor of length L and diameter D. How will the drift velocity of electrons change when? (i) V is doubled (ii) L is halved and (iii) D is halved, where in each case, the other two factors remain same. | 2 |
| 18. | A charge q is placed inside a sphere of radius ‘a’ filled with water and another charge 2q is placed inside cube of side ‘2a’ which is vacuumed inside. Find the ratio of the flux linked with the sphere to that linked with the cube. (Take relative permittivity of water as 80) | 2 |
| 19. | Write an expression for the magnetic force per unit length between two parallel thin current carrying wires with diagram. Hence define one ampere. OR Draw a diagram representing the behaviour of magnetic field lines for a (A) diamagnetic & (B) paramagnetic substance. For VI-Candidates State Gauss’s law of magnetism? Hence find the magnetic flux linked with the sphere enclosing a current carrying solenoid? | 2 |
| 20. | Prove that the speed with which the electron revolves in nth orbit is proportional to (1/n). OR How does the impact parameter affect the trajectory of a α – particles scattered by a heavy nucleus? What is the value of the impact parameter for head on collision of α – particles with the nucleus? | 2 |
| 21. | Justify how does the stopping potential in photoelectric emission depends upon (i) Intensity of the incident radiation (ii) frequency of incident radiation | 2 |
SECTION C
| Sl.No. | Questions | Marks |
| 22. | With the help of circuit diagrams explain working of the full wave rectifier. | 3 |
| 23. | State Ampere’s circuital law. Using this law, derive an expression for the magnetic field due to the infinitely long straight current carrying wire. OR
| 3 |
| 24. | Explain briefly, with the help of a circuit diagram, how a p-n junction diode works as a full wave rectifier. Explain its working. Draw the input and output waveforms. | 3 |
| 25. | A compound microscope consists of an objective lens of focal length 0.82 cm and an eyepiece lens of focal length 2.9 cm. An object is placed 0.91 cm from the objective lens. The image is formed at the near point (25 cm) from the eye. (I) Calculate the angular magnification of the microscope. (II) Draw the ray diagram of the compound microscope in normal adjustment. | 3 |
| 26. | Define self-inductance and give its SI unit. Derive an expression for the selfinductance of a long, air-cored solenoid of length l, cross-sectional area A and having N number of turns. OR A solenoid has a core of material with relative permeability 200. The windings of the solenoid are insulated from the core and carry a current of 1A. If the number of turns is 2000 per metre, calculate (A) magnetic intensity, (B) magnetic field & (C) magnetisation | 3 |
| 27. | Draw the reflected wave front for a plane wave front incident on a plane reflecting surface. Hence verify the laws of reflection using Huygen’s principle. For VI Candidates (I) Define wave front? (II) Define wavelet? (III) What will be the shape of the wave front intercepted by a large reflecting type telescope on earth, due to a star far-away from our solar system? | 3 |
| 28. |
(A) What will be the shape of the path followed by the given charged particle? (B) At what point will it cross the X-axis? (C) What will be the kinetic energy of a particle when it enters the fourth quadrant? | 3 |
SECTION D
| Sl.No. | Questions | Marks |
| 29. | When an external voltage is applied across a semiconductor diode such that p-side is connected to the positive terminal of the battery and n-side to the negative terminal it is said to be forward biased. The applied voltage mostly drops across the depletion region and the voltage drop across the p-side and n-side of the junction is negligible. When an external voltage is applied across the diode such that n-side is positive and p-side is negative, it is said to be reverse biased. The applied voltage mostly drops across the depletion region. (I) Ge and Si diodes start conducting at 0.3 V and 0.7 V respectively. In the following figure if Ge diode connections are reversed, the value of Vo changes by (assume that the Ge diode has large breakdown voltage) (A) 0.2 V (B) 0.4 V (C) 0.6 V (D) 0.8 V
| 4 |
| 30. | A pure semiconductor like Ge or Si , when doped with a small amount of suitable impurity, becomes an extrinsic semiconductor. In thermal equilibrium, the electron and hole concentration in it are related to the concentration of intrinsic charge carriers. A p-type or n-type semiconductor can be converted into a p-n junction by doping it with suitable impurity. Two processes: diffusion and drift, take place during formation of a p-n junction. A semiconductor diode is basically a p-n junction with metallic contacts provided at the ends for the application of an external voltage. A p-n junction diode allows currents to pass only in one direction when it is forward biased. Due to this property, a diode is widely used to rectify alternating voltages in half-wave or full wave configuration. I) When Ge is doped with pentavalent impurity, the energy required to free the weakly bound electron from the dopant is about (a) 0.001 eV (b) 0.01 eV (c) 0.72 eV (d) 1.1 eV
(III) During the formation of a p-n junction, (a) electrons diffuse from p-region into n-region and holes diffuse from n - region into p -region. (b) both electrons and holes diffuse from n -region into p-region. (c) electrons diffuse from n-region into p-region and holes diffuse from pregion into n-region. (d) both electrons and holes diffuse from p-region into n-region. (IV) Initially during the formation of p-n junction: (a) Diffusion current is large and drift current is small. (b) Diffusion current is small and drift current is large. (c) Both the diffusion and the drift currents are large. (d) Both the diffusion and the drift currents are small. | 4 |
SECTION E
| Sl.No. | Questions | Marks |
| 31. | (A) Derive lens maker’s formula. (B) Equi-convex lenses are to be manufactured from a glass of refractive index 1.55, with both faces of the same radius of curvature. What is the radius of curvature required if the focal length is to be 10cm? OR
Find: (i) the output voltage across the load circuit (ii) the current flowing through the load circuit (iii) the power supplied to the load circuit by the transformer (B) State the working principle of a transformer and explain how it is a key component in the transfer of electrical power over long distances. | 5 |
| 32. | (A) A dielectric slab of thickness t, is introduced between the plates of parallel plate capacitor of area A and separation d (where t<d). Find an expression for the capacitance with the dielectric slab. (B) A copper sphere of capacitor C is dropped in the ocean. Will the capacitance of the sphere increase, decrease or remain the same? Justify. (C) A capacitor is connected across a source of potential difference V and then the separation ‘d’ between the plates is increased using an insulating stick. Plot ‘V’ vs ‘d’ graph for the given capacitor. OR (i)An electric dipole is held in a uniform electric field. Using a suitable diagram shows that it does not undergo any motion. Derive the expression for the torque acting on it. (ii) What would happen if the field is non-uniform? (iii) What would happen if the external electric field is increasing (a) parallel to the Electric dipole moment and (b) anti-parallel to Electric dipole moment? | 5 |
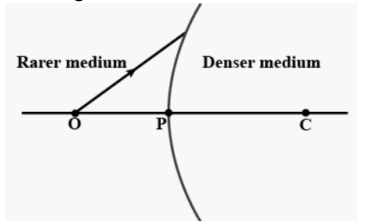
| 33. | (i)Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the image formation by an astronomical telescope in normal adjustment. (ii) Define magnifying power of an astronomical telescope in normal adjustment (i,e, when the final image is formed at infinity). (iii) A small telescope has an objective lens of focal length 144cm and an eyepiece of focal length 6cm.What is the magnifying power of the telescope? What is the separation between objective and eyepiece? OR A spherical surface of radius of curvature R, separates a rarer and a denser medium as shown in the figure.
Complete the path of the incident ray of light, showing the formation of a real image. Hence derive the relation connecting object distance ‘u’, image distance ‘v’ radius of curvature R and the refractive indices n1 and n2 of two media. Briefly explain how the focal length of a convex lens changes, with increase in wavelength of incident light. | 5 |
To download the complete question paper in the pdf format, click on the link below:
CBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper 2026: Download PDF |
CBSE Class 12 Exam Time Table 2026
The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has released the final Class 12 Date Sheet for the 2026 board exams, which are scheduled to be held from February 17 to April 10, 2026. The exams will be conducted in the traditional offline (pen and paper) format across designated centers in India and abroad. Students can directly download the official date sheet PDF from the CBSE website (cbse.gov.in) to better structure their study plans and strategically manage the gap days between subjects.
Also Check:

Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation