Key Points
- The Middle East connects Africa, Asia, and Europe, acting as a global crossroads.
- The region holds over 50% of the world's oil and 40% of its natural gas reserves.
- Key waterways like the Suez Canal and Strait of Hormuz are vital for global trade.
Do you know that modern-day Iraq was once home to the world's oldest civilisation, Mesopotamia? Also, Egypt is home to the last of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World still standing: the Great Pyramid of Giza.
All these countries come under a single band called the Middle Eastern Countries, which is not just a single entity but consists of around 26 countries. The reason behind this name, ‘Middle East’, is not because it is in the middle of the eastern side of the world.
The term originated from a Eurocentric perspective, coined by Europeans, to describe the land which covers the Southern part of Europe, Southwest Asia, and the Northern part of Africa, creating a middle ground for the Europeans.
Another reason was that the Europeans divided Asia to understand the distance between them: the Near East (Ottoman Empire/Balkans), the Middle East (Arabia, Persia, Central Asia), and the Far East (China, Japan).
This term gained popularity because of U.S. strategist Alfred Thayer Mahan. Additionally, the Middle East is frequently referred to as the "crossroads of the world", as it links Africa, Asia, and Europe.
In this article, we will explore the countries that make up this vibrant area, their unique features, and the facts that set each one apart.
Middle East Countries
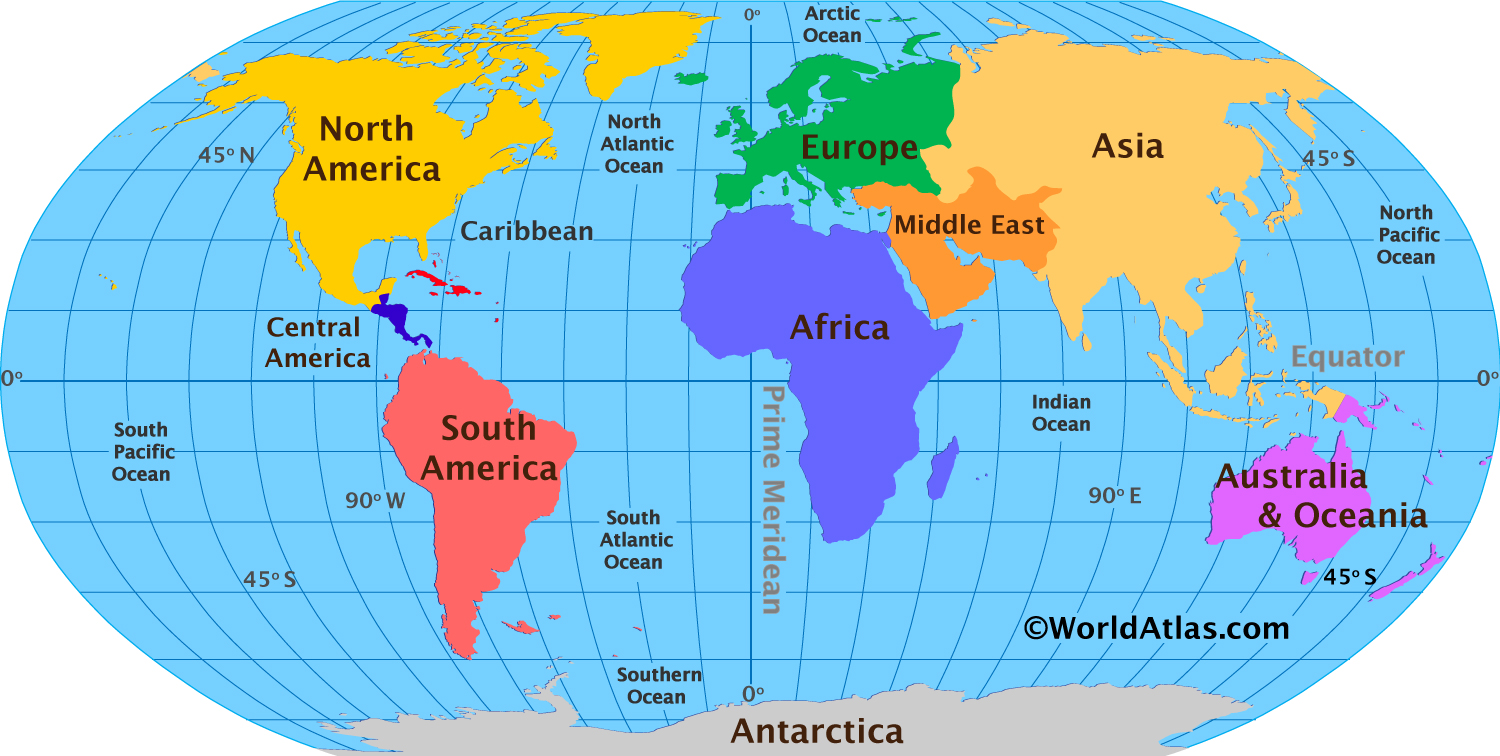
The Middle East is a unique region that spans two continents. It acts as a connection between major landmasses and bodies of water.
Its geography is shaped by its location at the intersection of three continents. The Middle East spans across:
- Asia: Most Middle Eastern countries are located in Southwest Asia (often called Western Asia).
- Africa: Egypt is the primary gateway to Africa, though the broader "MENA" (Middle East and North Africa) definition includes nations such as Libya, Algeria, and Morocco.
- Europe: Turkey is a country that spans two continents. A small part of it, called East Thrace, is in Southeast Europe.
Surrounding Seas and Oceans

The region is almost surrounded by water, which has historically made it a centre of global trade.
- The Levant countries, which include Israel, Lebanon, and Syria, as well as the northern coasts of Egypt, Libya, and Turkey, are surrounded by the Mediterranean Sea.
- The Red Sea separates the Arabian Peninsula from Northeast Africa.
- The northern coast of Turkey is bordered by the Black Sea.
- The Caspian Sea borders northern Iran and is the world's largest inland body of water.
- The Arabian Sea, which is located to the south, connects the region to the larger Indian Ocean.
Oceans:
- The Middle Eastern region touches the Indian Ocean through the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Aden.
Strategic Gulfs and Waterways
- The Persian Gulf is important for global oil shipping. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia, the UAE, Qatar, Kuwait, Iraq, and Iran.
- The Suez Canal is an important human-made waterway in Egypt. It links the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea.
- The Strait of Hormuz is the narrow entry point to the Persian Gulf. It is one of the most important oil checkpoints in the world.
List of Middle East Countries with Capitals
Here is the complete list of the Middle East countries in the world:
| S. No | Country | Capital | Currency | Area (Sq km) |
| 1 | United Arab Emirates | Abu Dhabi | UAE Dirham (AED) | 83,600 |
| 2 | Algeria | Algiers | Algerian Dinar (DZD) | 2,381,741 |
| 3 | Jordan | Amman | Jordanian Dinar (JOD) | 89,342 |
| 4 | Turkey | Ankara | Turkish Lira (TRY) | 783,562 |
| 5 | Greece | Athens | Euro (EUR) | 131,957 |
| 6 | Iraq | Baghdad | Iraqi Dinar (IQD) | 438,317 |
| 7 | Azerbaijan | Baku | Azerbaijani Manat (AZN) | 86,600 |
| 8 | Lebanon | Beirut | Lebanese Pound (LBP) | 10,452 |
| 9 | Egypt | Cairo | Egyptian Pound (EGP) | 1,010,408 |
| 10 | Syria | Damascus | Syrian Pound (SYP) | 185,180 |
| 11 | Qatar | Doha | Qatari Riyal (QAR) | 11,586 |
| 12 | Pakistan | Islamabad | Pakistani Rupee (PKR) | 796,095 |
| 13 | Afghanistan | Kabul | Afghan Afghani (AFN) | 652,230 |
| 14 | Sudan | Khartoum | Sudanese Pound (SDG) | 1,861,484 |
| 15 | Kuwait | Kuwait City | Kuwaiti Dinar (KWD) | 17,818 |
| 16 | Bahrain | Manama | Bahraini Dinar (BHD) | 765 |
| 17 | Oman | Muscat | Omani Rial (OMR) | 309,500 |
| 18 | Cyprus | Nicosia | Euro (EUR) | 9,251 |
| 19 | Saudi Arabia | Riyadh | Saudi Riyal (SAR) | 2,149,690 |
| 20 | Morocco | Rabat | Moroccan Dirham (MAD) | 446,550 |
| 21 | Yemen | Sanaa | Yemeni Rial (YER) | 527,968 |
| 22 | Georgia | Tbilisi | Georgian Lari (GEL) | 69,700 |
| 23 | Iran | Tehran | Iranian Rial (IRR) | 1,648,195 |
| 24 | Libya | Tripoli | Libyan Dinar (LYD) | 1,759,540 |
| 25 | Tunisia | Tunis | Tunisian Dinar (TND) | 163,610 |
| 26 | Armenia | Yerevan | Armenian Dram (AMD) | 29,743 |
What are the Geopolitical and Economic Importance of the Middle East Countries?

Because of its strategic location and natural resources, the Middle East is a global powerhouse.
- With 40% of the world's natural gas and more than 50% of its oil, the region holds a large share of both. It is important for global energy and production.
- Since it is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia and Africa, goods and fuel must be transported globally through vital waterways such as the Suez Canal and the Strait of Hormuz.
- Apart from oil, many countries, including Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, are investing and expanding heavily in renewable energy, technology and tourism to build a modern economy.
- Furthermore, Middle Eastern countries are rich in major natural resources, including oil and natural gas. They also play an important role in world politics.
- As a result, major powers, such as the US, China and Russia, constantly compete for influence in the region due to their resources and strategic location.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation