Key Points
- Budget 2026-27 focuses on economic stability and inclusive growth.
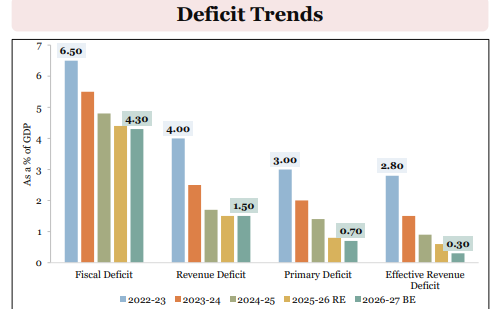
- Fiscal deficit for BE 2026-27 estimated at 4.3% of GDP.
- ₹20,000 crore allocated to CCUS technologies over 5 years.
The Union Budget 2026–27 was presented with the objective of maintaining economic stability while accelerating growth and development in a volatile global economic environment. The budget aims to strengthen domestic demand, boost capital expenditure, and promote inclusive growth. Key focus areas are Yuva Shakti, Agriculture, MSMEs, Employment, Green Energy, and Digital public infrastructure. It introduces important reforms to improve governance, fiscal management, and ease of doing business.
What is the Union Budget?
The Union Budget is the annual financial statement of the Government of India, presented every year by the Finance Minister in Lok Sabha, Parliament. It shows the government’s estimated receipts (income) and expenditure (spending) for the upcoming financial year. Through the budget, the government outlines its financial priorities and policy intent. The Union Budget, presented under Article 112 of the Indian Constitution. The objectives of the Union Budget are to promote economic growth, ensure social justice and inclusive development, and maintain fiscal discipline.
Where to Get Official Budget 2026 - 2027 PDF and FM Nirmala Sitharaman Speech?
The official Union Budget 2026–27 was presented by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on Sunday, February 1, 2026. You can access all official documents, including the PDF of the Budget Speech and the full budget datasets,
Budget 2026 - 2027 Highlights and Key Points -
Aim: Transform aspiration into achievement and Convert potential into performance
Core Focus Areas: Stability, Fiscal Discipline, Sustained Growth and Moderate Inflation
Yuva Shakti–Driven Budget: Government’s ‘Sankalp’
The budget focuses on the ''Poor, Underprivileged, and Disadvantaged'', with a strong emphasis on empowering youth as drivers of national development.
First Kartavya – Accelerate and Sustain Economic Growth
-
Enhance productivity and competitiveness
-
Build resilience against volatile global economic conditions
Second Kartavya – Fulfil Aspirations of the People
-
Build people’s capacity
-
Make citizens strong partners in India’s journey towards prosperity
Third Kartavya – Vision of Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas
-
Ensure every family, community, region, and sector has access to resources, amenities, and opportunities for meaningful participation in development.
Key Pillars of Growth and Development:
-
Sustaining Economic Growth
-
Strengthening the Foundations of Growth
-
People-Centric Development
-
Trust-based Governance
-
Ease of Doing Business and Ease of Living
-
Fiscal Matters
Key Features:
Viksit Bharat Budget Union Budget 2026–27: Fiscal Consolidation and Budget Estimates:
-
Debt-to-GDP ratio estimated at 55.6% of GDP in BE 2026–27, compared to 56.1% of GDP in RE 2025–26.
-
Fiscal deficit for BE 2026–27 estimated at 4.3% of GDP, lower than 4.4% of GDP in BE 2025–26.
-
Non-debt receipts estimated at ₹36.5 lakh crore in BE 2026–27.
-
Total expenditure estimated at ₹53.5 lakh crore in BE 2026–27.
-
Centre’s net tax receipts estimated at ₹28.7 lakh crore in BE 2026–27.
-
16th Finance Commision: The The Government has accepted the recommendation of the Commission to retain the vertical share of devolution at 41%. ▪ Provision ₹1.4 lakh crore to the States for the FY 27 as Finance Commission Grants. These include Rural and Urban Local Body and Disaster Management Grants.
Rupee Comes From: Revenue Sources
The government's income for FY 2026–27 is balanced between tax receipts and liabilities:
| Source | Percentage (%) |
| Borrowings & Other Liabilities | 24% |
| Income Tax | 21% |
| Corporation Tax | 18% |
| GST & Other Taxes | 15% |
| Non-Tax Receipts | 10% |
| Union Excise Duties | 6% |
| Customs | 4% |
| Non-Debt Capital Receipts | 2% |
III. Rupee Goes To: Expenditure Allocation
The Budget prioritizes state support and debt servicing:
| Expenditure Category | Percentage (%) |
| States' Share of Taxes & Duties | 22% |
| Interest Payments | 20% |
| Central Sector Schemes | 17% |
| Defence | 11% |
| Centrally Sponsored Schemes | 8% |
| Finance Commission & Other Transfers | 7% |
| Other Expenditure | 7% |
| Major Subsidies | 6% |
| Pensions | 2% |
Budget 2026-27: Government Total Receipts and Expenditure
Government Receipts (Where the Money Comes From):
The government expects a robust increase in collections, particularly in the revenue segment.
-
Revenue Receipts: Estimated at ₹35.3 lakh crore for 2026-27 (BE), up from the revised estimate of ₹33.4 lakh crore in the previous year.
-
Capital Receipts: Budgeted at ₹18.1 lakh crore for 2026-27 (BE), showing a steady climb to fund long-term assets.
Government Expenditure (Where the Money Is Spent):
The focus remains heavily on "Effective Capital Expenditure" to drive the multiplier effect in the economy.
-
Revenue Expenditure: Planned at ₹41.3 lakh crore, covering the day-to-day operational costs, subsidies, and interest payments.
-
Effective Capital Expenditure: Reaching a new high of ₹17.1 lakh crore for 2026-27 (BE). This is the core "growth engine" of the budget, focusing on building roads, railways, and digital infrastructure.
| Category | 2025-26 (RE) | 2026-27 (BE) | % Change (Approx) |
| Total Receipts | ₹49.6 | ₹53.4 | +7.6% |
| Revenue Receipts | ₹33.4 | ₹35.3 | +5.7% |
| Capital Receipts | ₹16.2 | ₹18.1 | +11.7% |
| Effective CapEx | ₹14.0 | ₹17.1 | +22.1% |
Manufacturing Sector: as Strategic and Frontier sector:
-
Biopharma SHAKTI: India as global Biopharma Manufacturing Hub to build the ecosystem for domestic production of biologists and biosimilars.
-
Indian Semiconductor Mission(ISM) 2.0
-
Electronics Components Manufacturing Scheme
-
Dedicated Rare Earth Corridors in Odisha, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu
-
Three Dedicated Chemical Parks
-
Scheme to revive 200 legacy industrial clusters
-
Container Manufacturing Scheme to be introduced with budgetary allocation of 10,000 crore over a 5 year period.
Tax Sector: Indirect Taxes and Direct Taxes
Ease of Doing Business with New Export Opportunities: Cargo clearance approvals to be processed through a single and interconnected digital window, Customs Integrated System (CIS) to be rolled out within 2 years as a single, integrated, and scalable platform for all customs processes.
Complete removal of the current value cap of ₹10 lakh per consignment on courier exports and Fish catch by Indian fishing vessels in the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) or on the High Seas to be made duty-free.
Customs Duty Exemptions: Basic customs duty exemption on components and parts required for the manufacture of civilian, training, and other aircraft. Facilitation of sales by eligible manufacturing units in Special Economic Zones (SEZs) to the Domestic Tariff Area (DTA) at concessional rates of duty.Increase in limit for duty-free imports of specified inputs used for processing seafood products for export from 1% to 3% of FOB value of the previous year’s export turnover.Extension of duty-free imports of specified inputs (currently available for exports of leather or synthetic footwear) to exports of shoe uppers as well.
High-Powered ‘Education to Employment and Enterprise’
High-Powered ‘Education to Employment and Enterprise’ High-Powered ‘Education to Employment and Enterprise’ Strategic Objectives
-
Establishment of Committee: A high-powered "Education to Employment and Enterprise" Standing Committee is being set up.
-
Focus on Services Sector: The committee will recommend measures focused on the Services Sector as the primary driver for "Viksit Bharat".
-
Global Leadership Goal: The initiative aims for India to become a global leader in services, targeting a 10% global share by 2047.
-
AI and Skills: Specifically, the committee will assess how Artificial Intelligence (AI) affects jobs and evolving skill requirements.
MSMEs:
Three pronged approach to help them grow as ‘Champions’: Equity support, Liquidity support &Professional support
Financial Support for SMEs and Micro Enterprises
-
SME Growth Fund: A new ₹10,000-crore fund has been proposed to incentivize and develop "champion" small and medium enterprises based on specific growth criteria.
-
Self-Reliant India (SRI) Fund: The government announced a ₹4,000-crore top-up for this fund in FY27 to continue providing equity support to micro enterprises.
-
Legacy Cluster Rejuvenation: A scheme will be launched to revive 200 legacy industry clusters to improve their productivity and global competitiveness.
India’s Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming and Comics(AVGC):
India’s Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming and Comics(AVGC), sector is a growing industry, projected to require 2 million professionals by 2030. I propose to support the Indian Institute of Creative Technologies, Mumbai in setting up AVGC Content Creator Labs in 15,000 secondary schools and 500 colleges
Orange Economy (AVGC-XR)
-
National Hub: IICT Mumbai operationalized as the Center of Excellence for Animation, Visual Effects, and Gaming.
-
Skill Pipeline: Establishing creator labs in 15,000 schools and 500 colleges.
-
Goal: Preparing a workforce for a sector projected to need 2 million professionals by 2030.
Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage (CCUS) technologies:
an outlay of ₹20,000 crore over the next 5 years in Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage (CCUS) technologies to scale up and achieve higher readiness levels in end-use applications across As outlined in the Union Budget 2026-27, here is the abstract for the Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) and Industrial Decarbonization initiatives, CCUS Outlay:
-
₹20,000 crore over 5 years for Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage technologies.
-
Sectors: Target hard-to-abate industries (Steel, Cement, Fertilizers, Refining).
-
Carbon Market: Carbon Credit Trading Scheme (CCTS) compliance mechanism starts in 2026.
Textile Sector: integrated program with five sub parts:
-
National Fibre Scheme
-
Textile Expansion and Employment Scheme
-
National Handloom and Handicraft Programme
-
Text-ECON Initiative
-
SAMARTH 2.0
Comprehensive Reforms To Creating Employment, Boosting Productivity & Accelerating Growth:
Over 350 reforms have been rolled out since Independence Day 2025
- Scaling up manufacturing in seven strategic and frontier sectors
- Rejuvenating legacy industrial sectors
- Creating Champion MSMEs
- Developing a powerful push for infrastructure
- Ensuring long-term security and stability
- Developing City economic regions
Tourism Sector: Expanding Economy through Strengthening Tourism
-
Launch of a scheme to support States in establishing five Regional Medical Hubs in partnership with the private sector.
-
These Medical Hubs will include AYUSH Centres, Medical Value Tourism Facilitation Centres, and infrastructure for diagnostics, post-care, and rehabilitatio
-
Setting up of a National Institute of Hospitality by upgrading the existing National Council for Hotel Management and Catering Technology (NCHMCT).
Empowering Divyangjan:
-
Divyangjan Kaushal Yojana launched to ensure dignified livelihood opportunities through industry-relevant and customised training, tailored to the specific needs of each divyang group.
-
Divyang Sahara Yojana to support the Artificial Limbs Manufacturing Corporation of India (ALIMCO) for scaling up production of assistive devices, with greater investment in R&D and AI integration.
-
Strengthening of PM Divyasha Kendras and support for setting up Assistive Technology Marts as modern retail-style centres to improve accessibility and service delivery.
Health Care Sector: To create a new range of skilled career pathways for our youth
-
Setting up of 3 new All India Institutes of Ayurveda to strengthen traditional healthcare education and services.
-
Addition of 1,00,000 Allied Health Professionals (AHPs) over the next 5 years to address workforce shortages in the health sector.
-
Launch of a scheme to support States in establishing 5 Regional Medical Hubs.
-
Training of 1.5 lakh caregivers to improve quality of care and support services.
-
Establishment of NIMHANS-2 to strengthen mental health infrastructure and services.
-
50% increase in capacity of District Hospitals through the establishment of Emergency and Trauma Care Centres.
Enter your Blink text here...
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation