Hundreds of millions of years ago, long before humans existed on Earth, the land on the planet looked a lot different from what we see today. All the continents that we see now, Asia, Africa, Europe, North America, South America, Australia, and Antarctica, were once one giant supercontinent named Pangaea. This massive landmass existed around 335 to 175 million years ago, during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras.
Scientists believe that Pangaea was surrounded by a single, huge ocean called Panthalassa. This ocean covered most of the Earth’s surface.
Discovery of Pangaea
The very idea of Pangaea was originally suggested by Alfred Wegener, a German meteorologist, in 1912. In his research, he noticed that the shapes of continents like South America and Africa seemed to fit together like puzzle pieces. He further found similar fossils, rock formations, and mountain ranges spread across continents that are now separated by vast oceans.
This led to the theory of continental drift, which explained that continents slowly move across Earth’s surface. Wegener’s idea was not fully accepted at first, but later discoveries in geology and plate tectonics proved him right.
What Did Pangaea Look Like?
Pangaea was shaped like a giant letter “C”, with most of the land clustered toward the Earth’s center.
-
The northern part was called Laurasia, which included what would later become North America, Europe, and Asia.
-
The southern part was called Gondwana, which included Africa, South America, Antarctica, Australia, and the Indian subcontinent.
In the middle of this supercontinent was a smaller sea called the Tethys Ocean, lying between Laurasia and Gondwana.
Life on Pangaea
Pangaea’s massive size had a direct influence on the climate and the life that lived on it. The interior areas of the continent were dry and desert-like because they were far from the sea. On the other hand, the coastal areas had more moderate climates.
During this time, early reptiles, amphibians, and some of the first dinosaurs lived on Pangaea. The connected land also made it easier for animals and plants to spread across different regions. Fossils found in South America and Africa, for example, show that the same species lived on both continents when they were still joined together.
ALSO READ: How did the First Mobile Phone Look Like? Check Key Interesting Fact
Why Did Pangaea Break Apart?
Around 175 million years ago, Pangaea began to split apart because of the movement of tectonic plates beneath the Earth’s surface.
-
First, Gondwana and Laurasia drifted away from each other.
-
Later, Gondwana itself broke apart, forming Africa, South America, Antarctica, and Australia.
-
The Indian sub-continent separated and slowly moved northward, eventually colliding with Asia, hence forming the Himalayan mountain range.
This slow process of breaking apart and drifting in different directions continued for millions of years and created the continents and oceans that we know today.
From One Land to Seven Continents
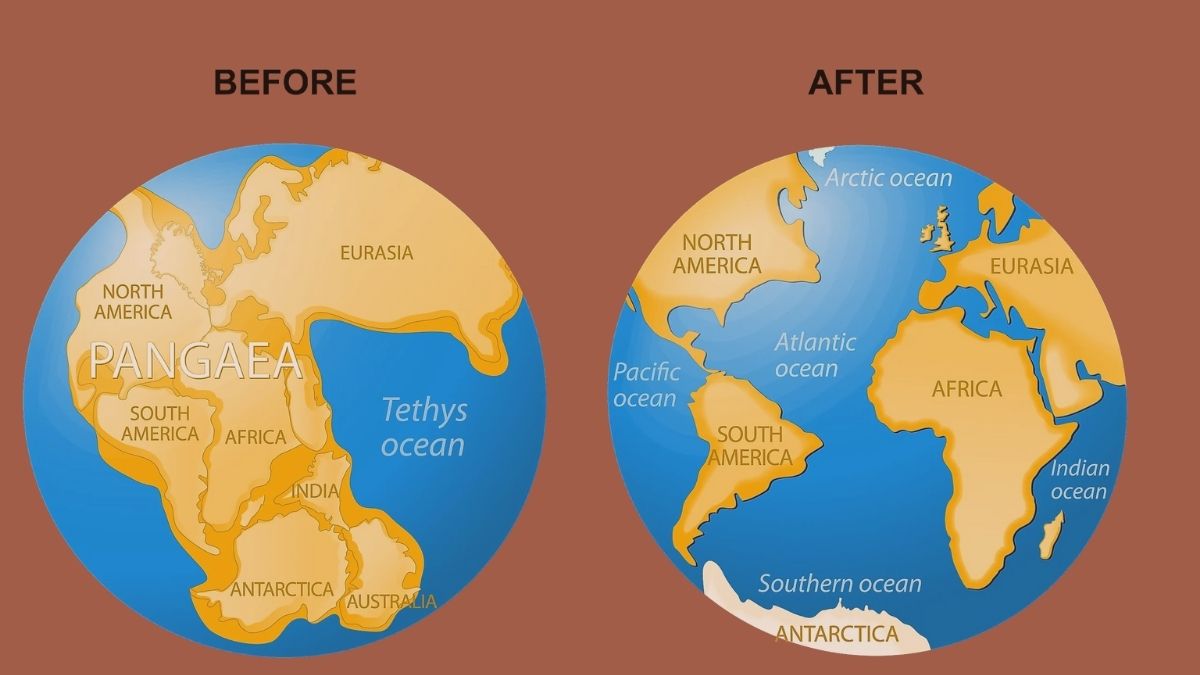
The story of Pangaea shows us how dynamic and ever-changing our planet Earth is. What was once a single supercontinent is now divided into seven continents that are spread across the globe.
Even today, these continents continue to move at a speed of a few centimeters per year. It is believed that millions of years from now, Earth may once again look completely different than it does in the present. It is also expected that the drifting of continents might result in the formation of a new supercontinent in the future.
Pangaea was not just a giant landmass; it was the starting point of Earth’s modern continents and a key chapter in the story of our planet.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation