The Ganga River System is not just a geographical feature; it is the lifeblood of northern and eastern India, touching the lives of millions across its long and storied course. Revered in mythology, significant in history, and essential in daily life, the Ganga originates in the Himalayas and eventually drains into the Bay of Bengal, supporting agriculture, drinking water supply, transportation, and spiritual practices. This article delves into the origin, course, tributaries, and importance of this vast river system.
From where does the Ganga River originate?
Origin of the Ganga River
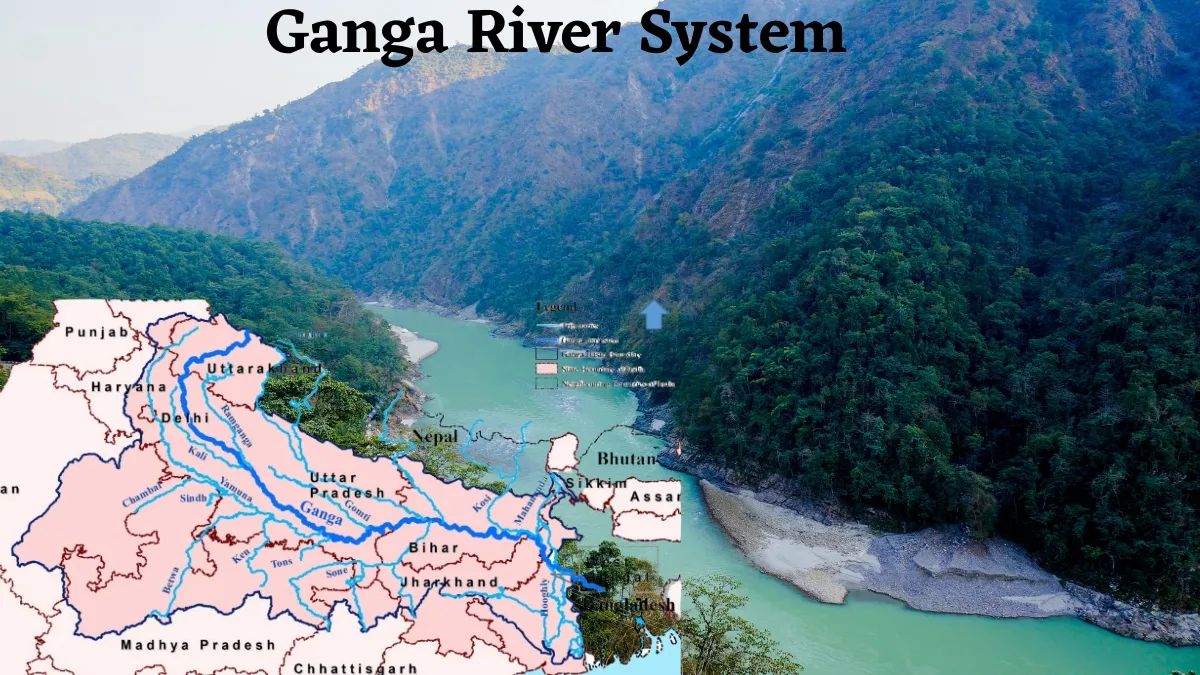
The Ganga River originates from the Gangotri Glacier in Uttarakhand, at a place called Gaumukh, where its headstream is known as the Bhagirathi. As it descends, it is joined by several streams, most notably the Alaknanda. The two rivers meet at Devprayag, where they are officially recognised as the Ganga.
States traversed by the Ganga River:
- Uttarakhand
- Uttar Pradesh
- Bihar
- Jharkhand
- West Bengal
With a catchment area of over 8.6 lakh sq km, it is among the largest river basins in the world and sustains nearly half of India’s population.
Course of the Ganga River
From the mountains of Uttarakhand to the plains of Bengal, the Ganga flows for 2,525 kilometres, with several major tributaries joining it along the way.
Key Stages of the Ganga's Course:
| Stage | Description |
| Source (Bhagirathi) | Originates from Gangotri Glacier (Gaumukh), Uttarakhand |
| Devprayag | Confluence of Bhagirathi and Alaknanda; officially becomes the Ganga |
| Haridwar | Enters the Indo-Gangetic plains |
| Prayagraj | Confluence with Yamuna at Sangam |
| Farakka Barrage | Divides into the Bhagirathi-Hooghly and Padma branches |
| Bay of Bengal | The Ganges merges with the Brahmaputra and Meghna in Bangladesh before draining out |
Major Tributaries of the Ganga River
The Ganga is joined by numerous tributaries, some from the Himalayas (northern tributaries) and others from the Peninsular plateau (southern tributaries). Here's a brief overview of the major tributaries:
Himalayan Tributaries (Northern)
| Tributary | Origin | Confluence Point with Ganga | Remarks |
| Yamuna | Yamunotri Glacier, Uttarakhand | Prayagraj | Longest tributary |
| Ghaghara | Mapchachungo Glacier, Tibet | Chhapra, Bihar | Known as Karnali in Nepal |
| Gandak | Nepal Himalayas | Sonepur, Bihar | Also called Narayani in Nepal |
| Kosi | Tibet and Nepal | Kursela, Bihar | “Sorrow of Bihar” due to floods |
Peninsular Tributaries (Southern)
| Tributary | Origin | State | Notable Info |
| Son | Amarkantak Plateau | Madhya Pradesh | Major right-bank tributary |
| Ramganga | Dudhatoli Hills | Uttarakhand | Joins the Ganga near Kannauj |
| Damodar | Chota Nagpur Plateau | Jharkhand | Earlier notorious for floods |
The Panch Prayags (Five Sacred Confluences)
The sacred Panch Prayag are the five holy confluences where tributaries meet the Alaknanda River in Uttarakhand before it becomes the Ganga.
| Prayag | Confluence of Rivers |
| Vishnuprayag | Alaknanda and Dhauliganga |
| Nandaprayag | Alaknanda and Nandakini |
| Karnaprayag | Alaknanda and Pindar |
| Rudraprayag | Alaknanda and Mandakini |
| Devprayag | Alaknanda and Bhagirathi (Ganga starts) |
Major Cities on the Banks of the Ganga
The Ganga nourishes some of India's most historic and populous cities, many of which are major cultural and spiritual centres:
| State | Cities |
| Uttarakhand | Rishikesh, Haridwar, Srinagar |
| Uttar Pradesh | Kanpur, Prayagraj, Varanasi, Mirzapur |
| Bihar | Patna, Bhagalpur |
| West Bengal | Howrah, Kolkata, Berhampore, Serampore |
Ganga-Brahmaputra Delta
Before emptying into the sea, the Ganga and Brahmaputra form the world’s largest delta, known as the Sundarbans Delta.
-
Shared by India and Bangladesh
-
Home to the Royal Bengal Tiger
-
Contains dense mangrove forests
-
Formed by the distributaries: Hooghly and Padma
Ecological and Cultural Significance
-
Supplies 33% of India’s surface water
-
Supports 60% of India’s irrigated agriculture
-
Central to Hindu rituals, with millions performing Ganga Aarti, ritual baths, and ashes immersion
-
Hosts important festivals like Kumbh Mela
Challenges and Conservation
Despite its divine status, the Ganga faces serious threats:
-
Industrial pollution
-
Untreated sewage discharge
-
Sand mining
-
Climate change-induced glacial melt
Key Conservation Initiatives
-
Namami Gange Programme
-
Ganga Action Plan (GAP)
-
Farakka Barrage Management
-
River cleaning missions and afforestation
Conclusion
The Ganga River System stands not only as a vital natural resource but also as a symbol of India’s civilisational heritage. Its waters quench the thirst of millions, nourish crops, and serve as the spiritual axis for countless pilgrims. However, to sustain its glory, active conservation, sustainable management, and public awareness are essential. The future of India’s ecological balance, water security, and cultural identity is intricately tied to the health of the Ganga.