Education shapes the future of a country. It builds knowledge, skills, and values in young minds. A strong education system helps people grow and succeed. It also supports the economy and improves the quality of life.
But what makes an education system the best? It's not just about test scores. The best systems focus on creativity, critical thinking, equal access, and student well-being. They prepare students for real-world challenges.
According to U.S. News, Denmark has one of the world's best education systems. It offers free education, trained teachers, and a stress-free learning environment. Other top countries include South Korea, Japan, and Canada.
In this article, we examine the world's top education systems. We'll explore what makes them great. We'll also see where India stands in global rankings. Is India catching up? What are its strengths and challenges? Let's find out.
Which Country's Education System Is Best?
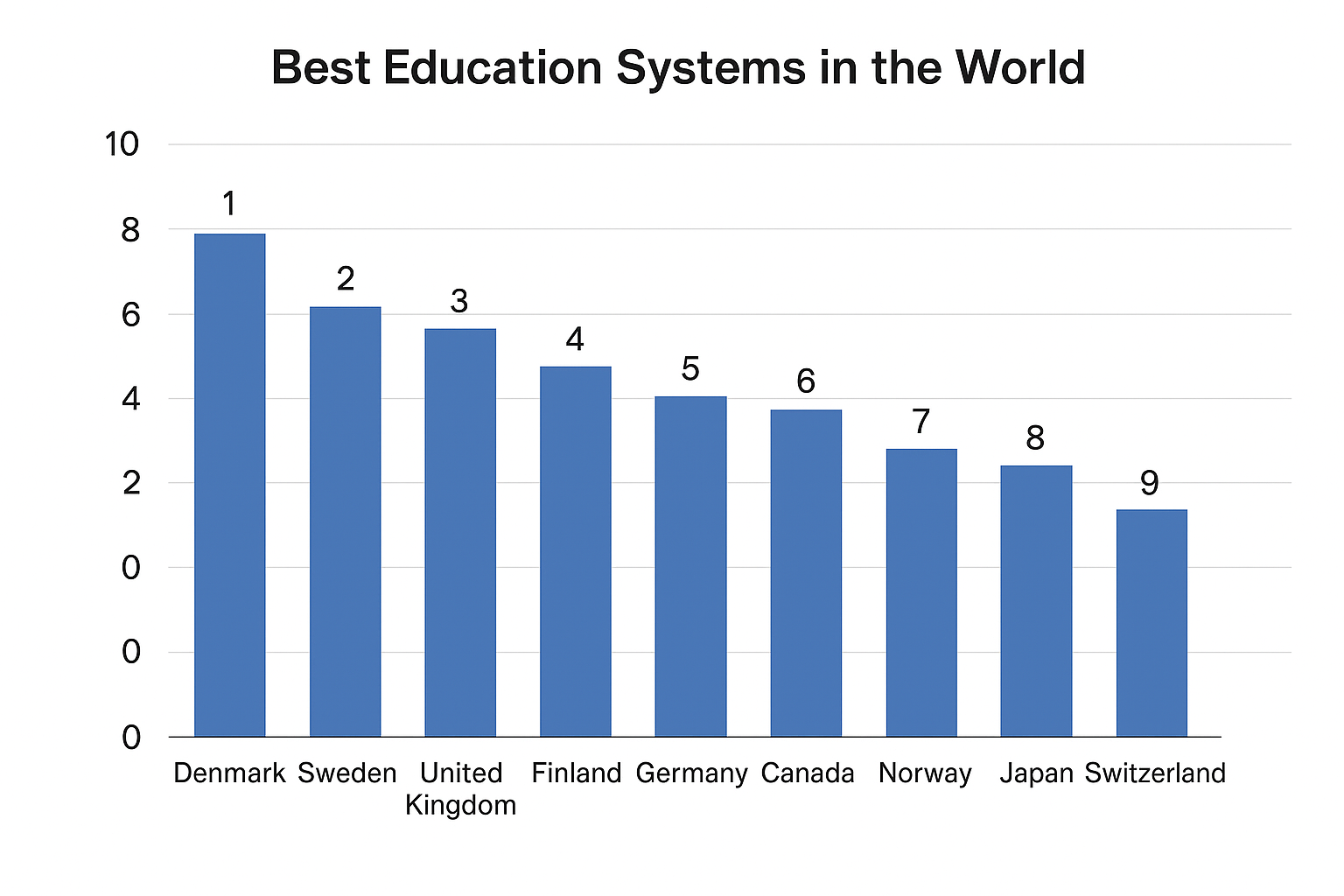
According to U.S. News, here is the list of the countries with the best education systems in the world:
| Ranking | Country | GDP | Population |
| 1 | Denmark | $404 billion | 5.95 million |
| 2 | Sweden | $593 billion | 10.5 million |
| 3 | United Kingdom | $3.34 trillion | 68.4 million |
| 4 | Finland | $300 billion | 5.58 million |
| 5 | Germany | $4.46 trillion | 84.5 million |
| 6 | Canada | $2.14 trillion | 40.1 million |
| 7 | Norway | $486 billion | 5.52 million |
| 8 | Japan | $4.21 trillion | 125 million |
| 9 | Switzerland | $885 billion | 8.85 million |
| 10 | Australia | $1.72 trillion | 26.6 million |
| 54 | India | $3.55 trillion | 1.43 billion |
1. Denmark
Denmark's education system is highly regarded for its commitment to free and accessible learning for all citizens.
It ranks #1 due to its inclusive approach, which emphasises critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration over rote memorisation. The system is well-funded, with a strong focus on early childhood education and vocational training.
A key feature is the "Folkeskole", a comprehensive public school system that all children attend from age 6 to 16. The high level of teacher autonomy and ongoing professional development also contribute to its success.
2. Sweden
Sweden's education system, ranked #2, is known for its focus on equity and quality. The government ensures all students, regardless of background, have access to excellent educational opportunities.
The system is decentralised, giving municipalities significant control over schools, which fosters local innovation.
A core principle is the promotion of lifelong learning, with a wide range of adult education programmes available. Additionally, the emphasis on student well-being and personalised learning plans helps to create an inclusive and supportive environment.
3. United Kingdom
The United Kingdom's education system, ranked #3, is highly diverse and globally influential. It is known for its prestigious universities and a strong tradition of academic excellence.
The system includes a mix of state-funded schools and private institutions. A key feature is the national curriculum, which sets clear standards for what is taught.
The UK's focus on standardised testing, such as GCSEs and A-levels, ensures a high level of accountability and provides a clear pathway to higher education. The country is also a central hub for international students.
4. Finland
Finland's education system, ranked #4, is internationally acclaimed for its unique and progressive approach.
The system is built on the principle of providing equal opportunities for all students, with no tuition fees from primary school to university. It stands out for its minimal standardised testing, instead relying on highly trained and respected teachers to assess student progress.
The emphasis is on play-based learning in early years and a holistic approach that prioritises student well-being, creative problem-solving, and a comfortable school environment.
5. Germany
Germany's education system, ranked #5, is known for its rigorous standards and strong vocational focus. It provides free education at all levels, including tertiary education, such as university.
A key feature is the structured tracking system in place after primary school, which directs students toward either an academic or vocational path. This system is designed to provide highly skilled workers for its robust economy.
The dual education system, which combines classroom instruction with on-the-job training, is a global model for vocational education and significantly contributes to the country's low youth unemployment rate.
6. Canada
Canada's education system, ranked #6, is highly regarded for its quality, accessibility, and multicultural focus. Education is primarily managed at the provincial level, resulting in some variations; however, the overall standard remains consistently high.
The system is publicly funded from elementary to post-secondary education. A key strength is its welcoming approach to immigrant students, with programmes designed to help them integrate successfully.
The emphasis on critical thinking and a diverse curriculum prepares students for a globalised world, contributing to Canada's strong economic and social development.
7. Norway
Norway's education system, ranked #7, is built on principles of equality and free access for all, from kindergarten to higher education. The government's significant investment in education ensures high-quality resources and well-compensated teachers.
The system promotes a collaborative and student-centred approach, focusing on social skills and critical thinking. There is a strong emphasis on outdoor activities and a holistic view of learning.
The "no-fail" policy in early grades, combined with a supportive learning environment, helps reduce student stress and fosters a love for learning.
8. Japan
Japan's education system, ranked #8, is known for its exceptional literacy rates and academic discipline.
The system is highly structured, with a strong emphasis on core subjects such as math, science, and Japanese. Students attend public schools, which are highly uniform in their standards and curriculum.
A key feature is the emphasis on group harmony and respect, with students actively participating in cleaning and maintaining their schools. The rigorous and competitive environment is a major driver of the country's technological advancements and economic success.
9. Switzerland
Switzerland's education system, ranked #9, is highly decentralised and internationally renowned for its quality. The system is managed at the cantonal (state) level, with a focus on practical skills and vocational training.
After primary school, students are tracked into different educational pathways, including academic and vocational.
The dual education system, combining apprenticeships with classroom learning, is a cornerstone of the economy, providing a skilled workforce. The multilingual environment and strong emphasis on quality and precision are hallmarks of Swiss education.
10. Australia
Australia's education system, ranked #10, is known for its high standards and diverse learning environment.
Education is managed by state and territory governments, leading to slight variations but a consistently high national standard. The system is publicly funded and offers a mix of public and private schools.
A key feature is the emphasis on both academic achievement and extracurricular activities. The country's universities are globally recognised and attract a large number of international students, contributing to a vibrant and multicultural educational landscape.
54. India
India's education system, while vast, faces challenges in achieving uniform quality and access across its huge population.
The government has prioritised education through initiatives like the Right to Education Act, making elementary education a fundamental right. The country serves as a central hub for science and technology, producing a significant number of engineers and IT professionals.
However, disparities exist between urban and rural areas, as well as between public and private schools. While the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and other top-tier universities are globally recognised, the overall quality of education and research still varies significantly.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation