In a major enhancement in the space capabilities of the country and naval communications, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO ) was able to launch GSAT-7R (also as CMS-03), the heaviest indigenously made advanced communication satellite, in Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), Sriharikota.
On the successful mission, as per the DD News, ISRO Chairman V. Narayanan described CMS-03 as “another shiny example of Aatmanirbhar Bharat,” crediting the achievement to the relentless efforts of ISRO teams across multiple centres despite challenging weather conditions.
Congratulations India, @isro has successfully launched the heaviest GEO communication satellite from Indian soil. The Indian space sector is soaring high to provide valuable services to the user community in and around the Indian region.
— ISRO (@isro) November 2, 2025
- Dr. V. Narayanan
Secretary,…
“The CMS-03 satellite is a multi-band communication satellite with coverage over a wide oceanic region, including the Indian landmass. It incorporates a host of new technologies and is designed to provide services for at least 15 years. The entire ISRO team deserves high praise for executing this complex mission flawlessly,” Narayanan said.
What a moment! #LVM3M5 lifts off with #CMS03, marking another milestone in India’s space journey. Relive the liftoff highlights pic.twitter.com/HOPEvYYljK
— ISRO (@isro) November 2, 2025
What is CMS-03 (GSAT-7R)?
As per the ISRO, India's LVM3 launch vehicle has successfully launched the CMS-03 communication satellite in its 5th operational flight (LVM3-M5) on November 02, 2025.
CMS-03 is a multi-band communication satellite that will provide services over a wide oceanic region, including the Indian landmass. This will be the heaviest communication satellite to be launched to Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) from Indian soil.
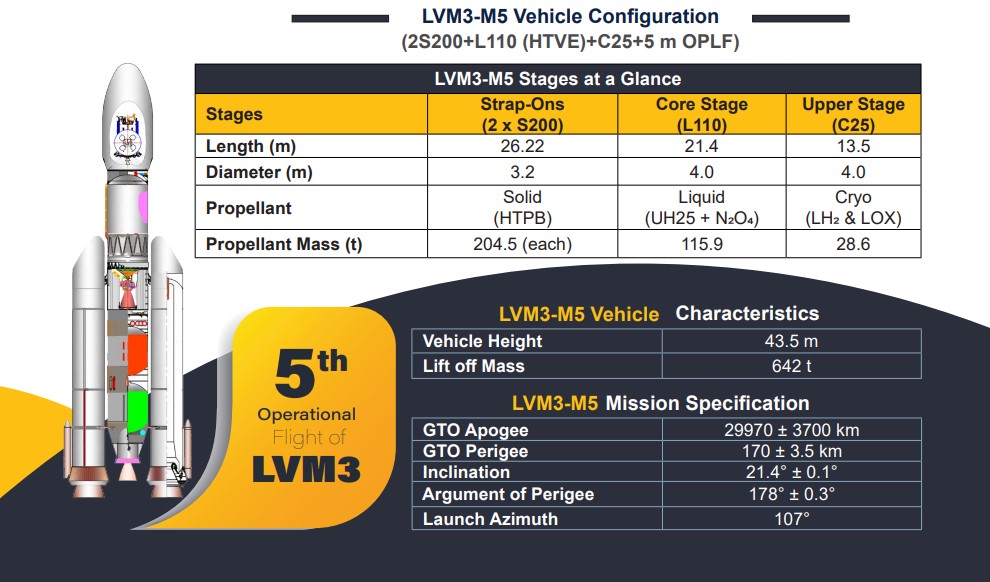
Source: ISRO
The previous mission of LVM3 launched the Chandrayaan-3 mission, in, India became the first country to land successfully near the lunar south pole.
What are the Most Important Facts of CMS-03 (GSAT-7R)?
Aboard: The CMS-03 was launched with the Mark-3 Launch Vehicle (LVM3-M5) on the fifth flight (LVM3-M5).
-
CMS-03 will be a multi-band communication satellite which will serve a wide oceanic terrain that comprises the Indian landmass.
-
CMS-03 is the heaviest communication satellite to have been launched to Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO), which weighs approximately 4400kg in India.
-
The last mission of LVM3, Chandrayaan-3, was the mission by which India was the first country to make a successful landing on the south pole of the moon.
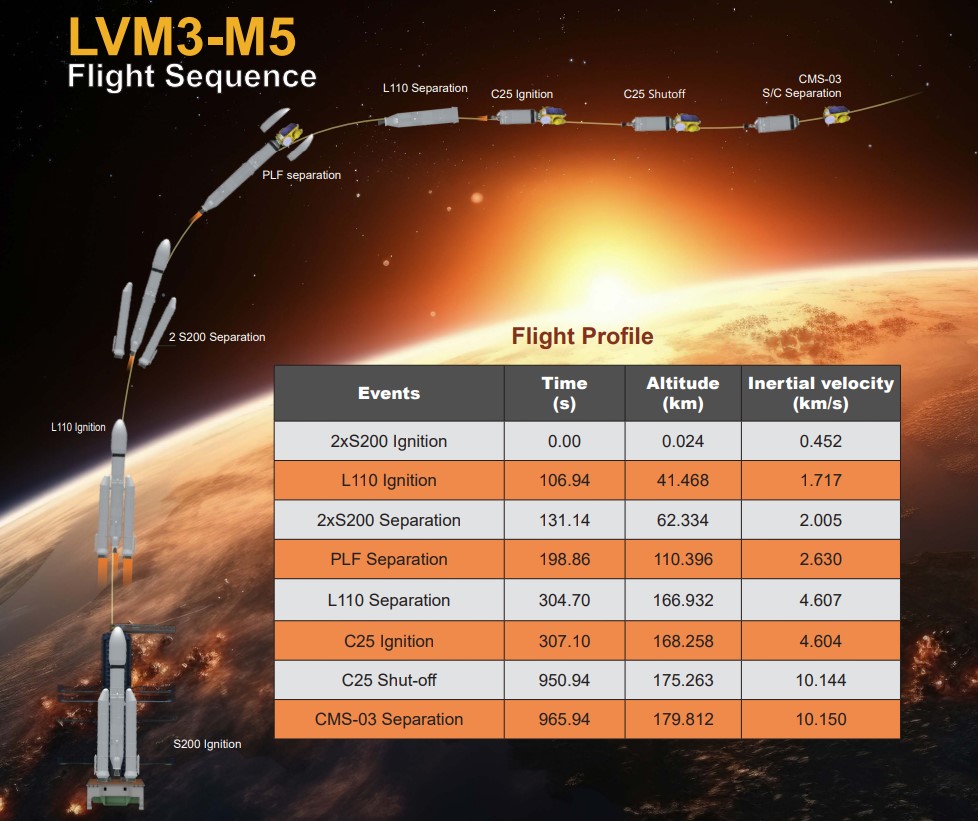
Source: ISRO
Technical Characteristics: The satellite is already in a GTO, and later it will shift into its final Geostationary Orbit with the help of its own propulsion system.
CMS-03, with a mission life of 15 years, is equipped with high-capacity multiband transponders that transfer voice, data and video signals, guaranteeing a secure and high-capacity communication of the Indian Navy in the Indian Ocean Region(IOR).
What is the Significance of the CMS-03 (GSAT-7R)?
The GSAT-7R will be in place of the 10-year-old GSAT-7 (Rukmini), which was launched in 2013 and is now nearing the expiry of its performance. The satellite is entirely made locally, and this is a sign of development in Aatmanirbhar Bharat.

Source: ISRO
The LVM3-M5 enhances the strategic freedom of India and minimises the dependency of vehicles of foreign origin on launching heavyweight packages like the European Ariane-5.
It also facilitates Gaganyaan preparations with features of displaying LVM3 heavy-lift capability and cryogenic re-ignition test of future missions.
Conclusion
The successful launch of GSAT-7R (CMS-03) marks a major milestone in India’s space and defence communication capabilities. It strengthens the Indian Navy’s secure communication network, showcases ISRO’s technological excellence, and reinforces India’s Aatmanirbhar Bharat vision by achieving self-reliance in launching advanced, heavy communication satellites through indigenous innovation and expertise.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation