Maths Formulas for Class 10: Mathematics is a foundational subject that can be both challenging and rewarding. Success in this field, especially for the CBSE Class 10 board exams, hinges on a strong command of its core principles. Formulas are the building blocks of mathematics; they provide a shortcut for solving complex problems and are essential for a quick and accurate approach. Therefore, whether a student loves the subject or struggles with it, mastering these fundamental equations is a non-negotiable step toward achieving proficiency. This mastery is best achieved not through rote memorization, but through consistent daily practice that embeds these concepts firmly in one's mind.
To assist students in their preparation, having a comprehensive and organized list of these important formulas is incredibly useful. This resource serves as a quick reference guide for revision, helps identify key areas of focus, and ensures that no crucial formula is overlooked. By using this list alongside regular practice, students can build confidence, reduce exam-day stress, and significantly improve their chances of performing well in the 2026 CBSE Class 10 board exam.
Check |
CBSE Class 10 Maths Formulas Chapter-Wise
Here is the chapter-wise list given, which you must read to get benefited. Read and revise to become a topper for Class 10 Maths.
Chapter 1 - Real Numbers
| Natural Numbers | N ={ 1, 2,3,4,5 … } |
| Whole Numbers | W={ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5… } |
| Rational Numbers | Those numbers which can be presented in the form of a/b are called Rational Numbers. |
| Real Numbers | Real Numbers can be found on a number line |
| LCM (P, Q, R) | P.Q.R.H.C.F(P, Q, R) / [HCF ( P, Q) . HCF( Q, R) . HCF ( P, R)] |
| HCF (P, Q, R) | P.Q.R.L.C.M(P, Q, R) / [LCM ( P, Q) . LCM ( Q, R) . LCM ( P, R)] |
Important* How to Attempt CBSE Class 10 Maths Exam 2025: Expert Tips for Scoring Maximum Marks
Chapter 2 - Polynomials
- (a+b)2 = a2+2ab+b2
- (a−b)2=a2−2ab+b2
- (x+a)(x+b) = x2+(a+b)x+ab
- a2−b2 = (a+b)(a−b)
- a3−b3 = (a−b)(a2+ab+b2)
- a3+b3 = (a+b)(a2−ab+b2)
- (a+b)3 = a3+3a2b+3ab2+b3
- (a−b)3 = a3−3a2b+3ab2−b3

Chapter 3 - Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Linear equation in one variable: ax +b =0, a≠0 and a&b are real numbers
- Linear equation in two variables: ax+ by+ c =0 , a≠0 & b≠0 and a,b & c are real numbers
- Linear equation in three variables: ax+ by+ cz= 0, a≠0 , b≠0, c≠0 and a,b,c,d are real numbers
- a1x+b1y+c1=0
- a2x+b2y+c2=0
Where a1, b1, c1, a2, b2, c2 are all real numbers and a12+ b12 ≠ 0, a22+ b22 ≠ 0
Chapter 4 - Quadratic Equations
x = (α, β) = [-b ± √(b2 – 4ac)]/2a provided b2 – 4ac >= 0
A quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 has
(i) two distinct real roots, if b2 – 4ac > 0,
(ii) two equal roots (i.e., coincident roots), if b2 – 4ac = 0, and
(iii) no real roots, if b2 – 4ac < 0
Chapter 5 - Arithmetic Progressions
The nth term of AP = nth term = a + (n-1) d
Sum of n terms in AP = Sn = n/2[2a + (n − 1) × d]
Sum of all terms in AP with the last term ‘l’ = n/2(a + l)
Chapter 6 - Triangles
Here,
A = Area of Triangle
B = Base of Triangle
H = Height of a Triangle
Area of Triangle = A = ½ (b × h) square units
Area of an Isosceles Triangle = 1/4 b√(4a2 – b2)
Area of a Right Triangle = A = 1/2 × Base × Height
Area of an Equilateral Triangle = A = (√3)/4 × side2
IMPORTANT | CBSE Class 10 Maths Blueprint 2025
Chapter 7 - Coordinate Geometry
- Distance Formula to find distance between two points P(x1,y1) and Q(x2,y2) is = √[(x2 – x1)2 + (y2 – y1)2 ]
- Distance of a point P(x, y) from the origin is = √x2 + y2
- The coordinates of the point P(x, y) which divides the line segment joining the points A(x1 , y1 ) and B(x2 , y2 ) internally in the ratio m1 : m2 = Section Formula = ((m1x2 + m2x1)/m1+ m2 , (m1y2 + m2y1)/m1+ m2)
- The mid-point of the line segment joining the points P(x1, y1) and Q(x2, y2 ) = [(x1+x2/2), (y1+y2/2)
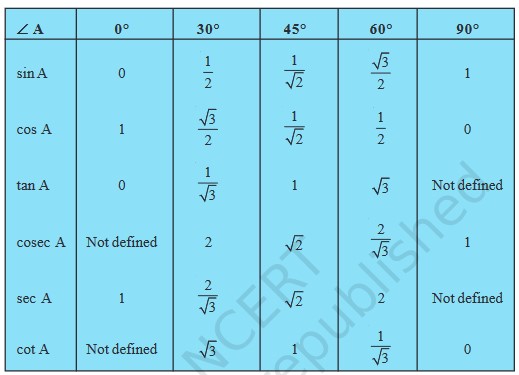
Chapter 8 - Introduction to Trigonometry
| Basic Trigonometric Formulas | |
| Property | Mathematical value |
| sin A | Perpendicular/Hypotenuse |
| cos A | Base/Hypotenuse |
| tan A | Perpendicular/Base |
| cot A | Base/Perpendicular |
| cosec A | Hypotenuse/Perpendicular |
| sec A | Hypotenuse/Base |
| Reciprocal Relations | |
| tan A | sin A/cos A |
| cot A | cos A/sin A |
| cosec A | 1/sin A |
| sec A | 1/cos A |
Trigonometry Table
Chapter 9 - Some Applications of Trigonometry
- sin(90°– θ) = cos θ
- cos(90°– θ) = sin θ
- tan(90°– θ) = cot θ
- cot(90°– θ) = tan θ
- sec(90°– θ) = cosecθ
- cosec(90°– θ) = secθ
Chapter 10 - Circles
When r = radius of the circle,
- Circumference of the circle = 2 π r
- Area of the circle = π r2
- Area of a sector of a circle with radius r and angle with degree measure θ = (θ/360) × π r2
- Length of an arc of a sector of a circle with radius r and angle with degree measure θ = (θ/360) × 2 π r
Chapter 11 - Areas Related to Circles
Area of segment of a circle = Area of the corresponding sector – Area of the corresponding triangle.
Chapter 12 - Surface Areas and Volumes
CUBOID
- Surface Area of a cuboid of length (l), breadth (b), and height (h) = 2 (lb + bh + lh)
- Lateral Surface Area of cuboid = 2 (l + b)h
CUBE
- Surface Area of a cube = 6 ✕ l2 where l is the length
- Lateral Surface Area of cube = 4 ✕ l2, where l is the length
- Volume of cube = l2
CYLINDER
- Total Surface Area of a Cylinder = 2πr (h+r)
- Lateral Surface Area of a Cylinder = 2πrh
- Volume of Cylinder = πr2 h
CONE
- Lateral Surface Area of Cone = πrL
- Total surface area of cone = πr ( L+ r)
- Volume of Cone = ⅓ (πr2 h)
- Volume of a frustum of a cone = 1/3 πh(r₁2 + r₂2 + r₁r₂)
SPHERE
- Surface Area of Sphere= 4 πr2
- Volume of Sphere = 4/3 (πr3)
Chapter 13 - Statistics
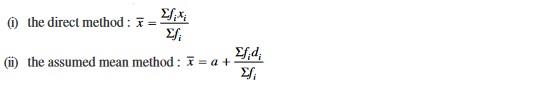

The mean for grouped data can be found by: l + (n/2-cf/f) × h.
Chapter 14 - Probability
- The theoretical (classical) probability of an event E, written as P(E), is defined as
P (E) = Number of outcomes favourable to E / Number of all possible outcomes of the experiment, where we assume that the outcomes of the experiment are equally likely
- The probability of a sure event (or certain event) is 1
- The probability of an impossible event is 0
- The probability of an event E is a number P(E) such that 0≤ PE≤ 1
Now you have the most important part prepared, check other resources and study material from the link below:
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Important Competency Based Questions 2025
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter-Wise Weightage 2025
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Deleted Syllabus 2024-25
IMPORTANT TOPICS SUBJECT-WISE | ||
Physics | Chemistry | Mathematics |
Social Science | ||
Biology | ||
|
| ||
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation